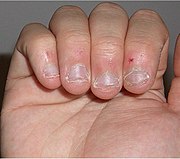
Onychophagia or nail biting is a common oral compulsive habit in children and adults, affecting around 30% of children between 7 to 10 years and 45% of teenagers.
Negative effects
Bitten fingertips can become very sensitive to pain, usually at the place the skin meets the edge of the nail. Hangnails are broken skin on the cuticle. When they are improperly removed, they are susceptible to microbial and viral infections producing whitlows. Saliva may then redden and infect the skin. Finally it may also result in the transportation of bacteria that are buried under the surface of the nail, or pinworms from anus region to mouth. Nail biting is also related to dental problems, such as gingival injury.
Regarding social effects the aesthetic aspect of the nail may affect employability, self-esteem, and interaction with other people.
Treatment
Behavioral treatments are based in discouraging the habit and replace it with a more constructive habit. The most common treatment, as it is cheap and widely available, is a special clear nail polish that has to be applied to the nails. It releases a bitter flavor on contact with the mouth which discourages the habit and has demonstrated its effectiveness. There are also mouthpieces that prevent biting.
Behavioral therapy is beneficial when simpler measures are not effective. Habit Reversal Training (HRT), seeks to "unlearn" the habit of nail biting and possibly replace it with a more constructive habit and has shown its effectiveness versus placebo both in children and adults. In addition to HRT, stimulus control therapy is used to both identify and then eliminate the stimulus that frequently triggers biting urges.
Finally nail cosmetics can help to ameliorate nail biting social effects.
Related disorders
Some related body-focused repetitive behaviors are dermatillomania (skin picking), dermatophagia (skin biting) or trichotillomania (urge to pull out hair).



No comments:
Post a Comment